Electric Bikes: Everything You Need to Know
Electric bikes, or e-bikes, represent the perfect fusion of traditional cycling and modern technology. These innovative vehicles feature battery-powered motors that assist your pedaling effort, making cycling more accessible, efficient, and enjoyable for a wider range of people. With rising concerns about climate change, urban congestion, and personal fitness, e-bikes have surged in popularity as versatile transportation solutions that address multiple needs simultaneously.
Whether you're looking to reduce your carbon footprint, cut commuting costs, or simply enjoy cycling with less physical strain, electric bikes offer compelling advantages over conventional transportation options. For the security-conscious cyclist, innovations like AirTag mounts can provide peace of mind against the growing concern of bicycle theft.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore everything from how electric bikes function and their various types to practical buying advice, security considerations, and maintenance tips to keep your investment running smoothly for years to come.
What are electric bikes and how do they work?
Electric bikes combine traditional bicycle components with an integrated electric motor system that provides pedaling assistance. Unlike motorcycles or scooters, most e-bikes still require the rider to pedal—the motor simply amplifies the human power input, making hills feel flatter and distances seem shorter.
At the heart of every electric bicycle is a rechargeable battery (typically lithium-ion) that powers an electric motor. This motor can be mounted in different locations: in the front hub, rear hub, or at the crankset (mid-drive). When activated, sensors detect your pedaling and trigger the motor to provide a predetermined level of assistance. Most models feature multiple assistance levels, allowing riders to balance battery conservation with the desired amount of boost.
Modern e-bikes typically include an onboard computer or control panel mounted on the handlebars. This interface displays vital information like current speed, battery level, assistance mode, and trip statistics. Many newer models even offer smartphone connectivity for navigation, fitness tracking, and firmware updates.
The key difference between conventional bicycles and their electric counterparts lies in versatility and accessibility. While traditional bikes rely solely on human power, electric cycles can adjust to your needs—offering minimal assistance when you want exercise or maximum support when tackling challenging terrain or long commutes.
Types of electric bikes: Pedelec, throttle, and more
Electric bikes come in several distinct varieties, each designed for different riding preferences and legal requirements:
- Pedal-assist (Pedelecs): These most common e-bikes provide motor assistance only when the rider is pedaling. Sensors detect pedaling motion and apply proportional power. In most regions, pedelecs limited to 20 mph (32 km/h) face fewer regulatory restrictions.
- Throttle-based e-bikes: Similar to scooters, these models can deliver power via a handlebar-mounted throttle without requiring pedaling. Many jurisdictions classify these differently from pedelecs, often with stricter regulations.
- Speed pedelecs (S-pedelecs): High-performance models capable of assisted speeds up to 28 mph (45 km/h), typically requiring registration, insurance, and helmet use in many regions.
- Class systems: In the US and some other countries, e-bikes are categorized into three classes based on their maximum assisted speed and control mechanism (pedal-assist vs. throttle).
Beyond these fundamental types, the market offers specialized electric bicycles for various applications: mountain e-bikes with robust suspension for off-road adventures, folding e-bikes for multi-modal commuters, cargo e-bikes capable of transporting heavy loads, and sleek urban models optimized for city navigation.
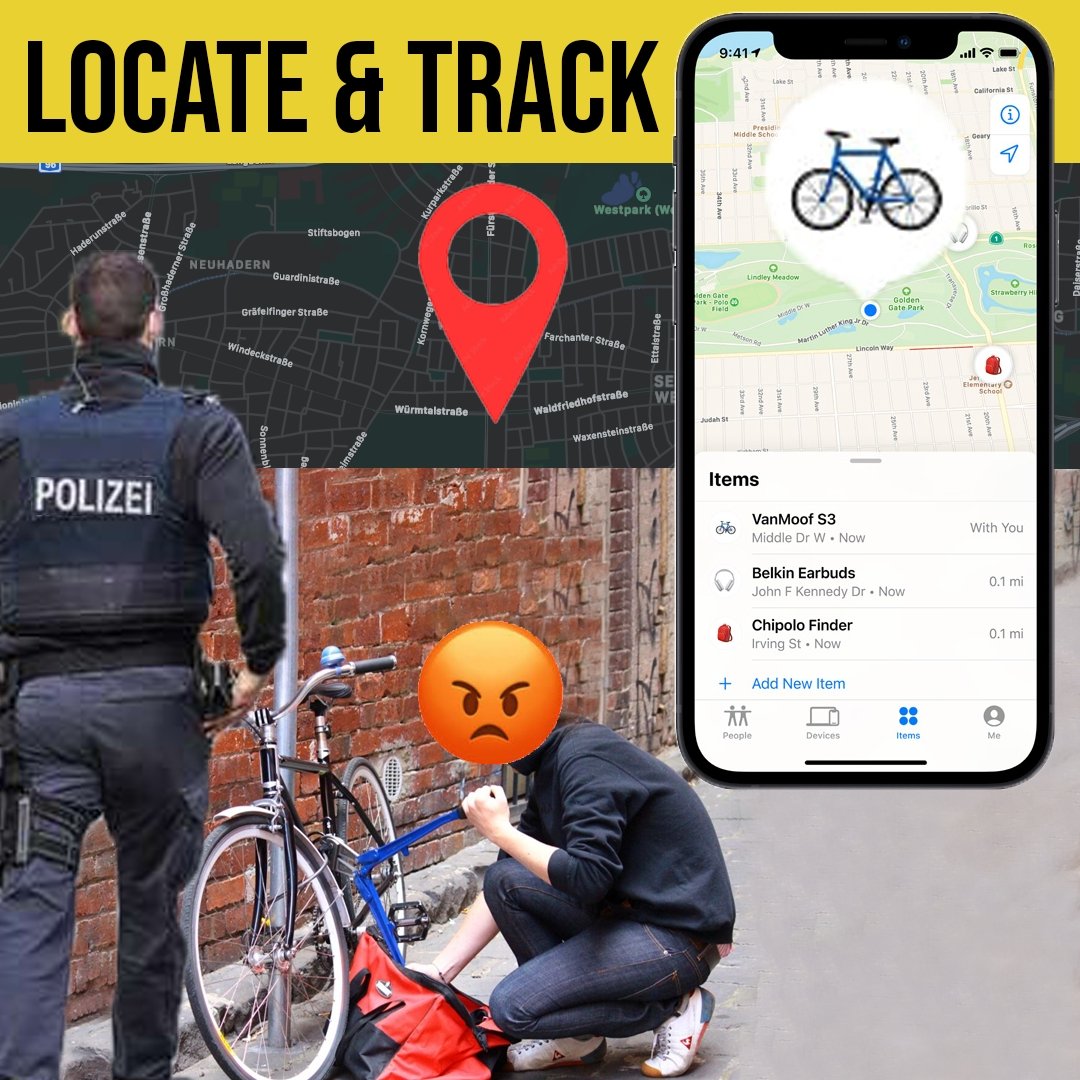
When exploring different types, consider investing in comprehensive security solutions like the Guards Armor Bike Mount for Apple AirTag, which cleverly disguises as a water bottle cage while providing hidden tracking capabilities for your valuable ride.
Key benefits of electric bikes
Electric bicycles offer multifaceted advantages that extend well beyond simple transportation. Understanding these benefits can help determine if an e-bike aligns with your lifestyle needs and values.
Environmental impact represents one of the most compelling advantages of e-bike adoption. With zero direct emissions, electric cycles provide a genuinely eco-friendly transportation alternative that reduces carbon footprint. Studies indicate that e-bikes produce approximately 2.5-5 grams of CO2 per kilometer (including battery production and electricity generation), compared to 150-250 grams for passenger cars. This remarkable efficiency translates into meaningful environmental protection when integrated into daily commuting routines.
Financial considerations further strengthen the case for e-bikes. While the initial purchase price exceeds that of conventional bicycles, operating costs remain minimal. The average e-bike costs mere pennies to charge fully, typically between $0.05-0.15 per charge depending on local electricity rates. Compared to automobile expenses (fuel, insurance, parking, maintenance), e-bikes can save commuters thousands of dollars annually. Many urban cyclists report recouping their initial investment within 6-18 months through reduced transportation costs.
Commuting transformation ranks among the most immediately noticeable benefits. E-bikes effectively eliminate many common cycling barriers: arriving sweaty at destinations, struggling with hills, headwinds, or longer distances. The pedal assistance makes maintaining consistent speeds easier, often resulting in more predictable commute times than both conventional cycling and car travel in congested areas. Studies show e-bike commuters typically travel 50-70% farther than traditional cyclists, expanding practical commuting range.
Accessibility represents perhaps the most significant social benefit of e-bike technology. The motor assistance democratizes cycling for people across age groups, fitness levels, and physical abilities. Older riders, those with joint issues, or individuals recovering from injuries can maintain cycling activity with appropriate assistance. This inclusivity aspect has made e-bikes particularly popular among riders returning to cycling after years away or those who previously considered cycling too physically demanding.
Health benefits, contrary to some misconceptions, remain substantial with e-bike use. Research consistently shows that while assistance reduces exertion, e-bike riders still engage in moderate physical activity, with most users spending more total time cycling than they would on conventional bikes. The adjustable assistance levels also allow riders to gradually build fitness by reducing motor support as personal strength improves.
Is an electric bike right for you?
Electric bikes particularly suit certain situations and needs. You might benefit from an e-bike if:
- Your commute spans 5-15 miles each way (too far for comfortable regular cycling, but perfect for e-bikes)
- You encounter significant hills or consistent headwinds during your typical rides
- You want to reduce car dependency without sacrificing mobility range
- You have joint issues, reduced fitness, or medical conditions that make conventional cycling challenging
- You need to arrive at destinations without requiring shower facilities
- You're seeking a low-impact way to build or maintain fitness
- You want to keep pace with more athletic cycling partners or family members
Many cyclists find that e-bikes don't replace traditional bicycles but complement them—serving different purposes within a versatile transportation strategy.
Buying guide: What to look for in an electric bike
Navigating the e-bike market requires understanding several key components that determine performance, reliability, and value. This systematic approach will help you make an informed purchase decision.
Motor systems form the heart of any electric bicycle, available in three primary configurations:
- Hub motors (front or rear wheel): Generally more affordable and simpler to maintain. Front hub designs offer better weight distribution but can affect handling; rear hub motors provide better traction but concentrate weight toward the back.
- Mid-drive motors: Positioned at the bicycle's central crankset, these premium systems offer superior weight distribution, more natural handling, and efficient power transfer through the bike's existing gears. They excel on varied terrain but typically cost more.
Motor power ratings range from 250W to 750W+ (legal limits vary by region). For most riders, 250-350W provides sufficient assistance for commuting and recreational riding, while heavier riders or those facing steep terrain might prefer 500W+ systems.
Battery considerations significantly impact range, weight, and convenience:
- Capacity: Measured in watt-hours (Wh), typical ranges span from 300Wh to 700Wh. Higher capacity extends range but increases weight and cost.
- Range: Most manufacturers advertise 20-80 miles per charge, but real-world performance depends on rider weight, terrain, assistance level, and weather conditions. A practical estimate: divide the battery capacity (Wh) by 15 to get a realistic range in miles under mixed conditions.
- Removability: Detachable batteries facilitate indoor charging and enhance security. Fixed batteries may offer cleaner design but limit charging flexibility.
- Charging time: Most batteries require 3-6 hours for full charging. Some premium models offer fast-charging capabilities.
Frame design and build quality deserve careful consideration. Purpose-built e-bike frames with integrated batteries offer cleaner aesthetics and better weight distribution than retrofit designs. Step-through frames provide easier mounting/dismounting, while traditional diamond frames may offer enhanced rigidity. Regardless of style, quality welds, clean cable routing, and robust component mounting points indicate attention to detail.
Component quality significantly impacts long-term satisfaction. Look for hydraulic disc brakes for reliable stopping power (especially important given e-bikes' higher speeds and weights), quality derailleur systems from established manufacturers like Shimano or SRAM, and puncture-resistant tires designed specifically for e-bike speeds and weights.
Display systems and controls range from basic LED indicators to sophisticated color touchscreens. At minimum, look for clear battery level indication, assistance level controls, and basic trip information. More advanced systems may include navigation, fitness metrics, and smartphone connectivity.
Price considerations span a wide spectrum: entry-level models start around $1,000-1,500, mid-range quality options typically cost $2,000-3,500, while premium models can exceed $5,000. While budget constraints matter, prioritize quality components and reliable brands over superficial features. Many owners report that investing in a quality model initially proves more economical than upgrading an inadequate bicycle later.
When finalizing your purchase, investigate warranty coverage (1-5 years is standard), dealer support networks (especially important for proprietary systems), parts availability, and user reviews focused on long-term reliability. Additionally, consider how you'll secure your investment against theft. As discussed in this guide on protecting bicycles from theft, combining physical locks with tracking technologies provides the most comprehensive security approach.
How to keep your electric bike safe and secure
Electric bikes represent significant investments, often costing several thousand dollars, making them attractive targets for thieves. Implementing comprehensive security measures is essential for protecting your property.
Understanding theft risk factors helps prioritize appropriate security measures. Urban environments, university campuses, and public transportation hubs represent particularly high-risk locations. Most thefts occur during brief periods when owners assume their bicycles remain safe—quick errands, coffee stops, or workplace parking. E-bikes face higher theft risk than conventional bicycles due to their higher value and ready resale market.
Physical security forms your first defense line. Invest in quality locks specifically designed for e-bikes:
- U-locks/D-locks: Provide excellent resistance against leverage attacks. Select models with at least 13-16mm hardened shackles.
- Chain locks: Offer flexibility for securing to various objects. Look for 10-14mm hardened links with protected lock mechanisms.
- Folding locks: Balance security and portability. Select models with independent certification ratings.
For maximum protection, employ the "two lock method"—securing the frame and rear wheel with a primary lock while using a secondary lock for the front wheel and frame. Always lock to immovable objects, preferably in well-lit, high-traffic areas with security cameras when possible.
Electronic tracking technologies provide crucial secondary protection. GPS trackers designed specifically for bicycles offer precise location monitoring but typically require subscription services. Bluetooth trackers like Apple AirTags provide more affordable alternatives by leveraging nearby smartphones for location reporting. For optimal security with minimal visibility to thieves, consider discrete mounting solutions like the Guards Armor Bike Mount for Apple AirTag, which conceals the tracker within what appears to be a standard bottle cage, using security screws to prevent unauthorized removal.
Insurance protection represents a vital final security layer. Options include:
- Specialized bicycle insurance: Offers comprehensive coverage specifically for bicycles with typically faster replacement processes.
- Homeowners/renters insurance: May cover bicycles but often with high deductibles and potential premium increases after claims.
- Manufacturer programs: Some premium brands offer integrated anti-theft protection programs.
When selecting coverage, verify policy details regarding e-bike components, replacement value calculations, and required documentation for claims (including proof of ownership, component serial numbers, and photos).
Secure storage solutions minimize risk during extended periods. For home storage, consider wall-mounted systems, dedicated bicycle lockers, or anchored ground/floor attachments. Many workplaces and residential buildings now offer secure bicycle rooms or monitored parking areas—utilize these whenever available. For overnight public storage, seek bicycle lockers or staffed facilities rather than leaving your e-bike unattended, even when locked.
Electric bike maintenance: Tips for longevity
Proper maintenance significantly extends your electric bicycle's useful life while ensuring optimal performance and safety. While e-bikes share many maintenance needs with conventional bicycles, their electrical components require additional attention.
Battery care represents the most crucial aspect of e-bike maintenance.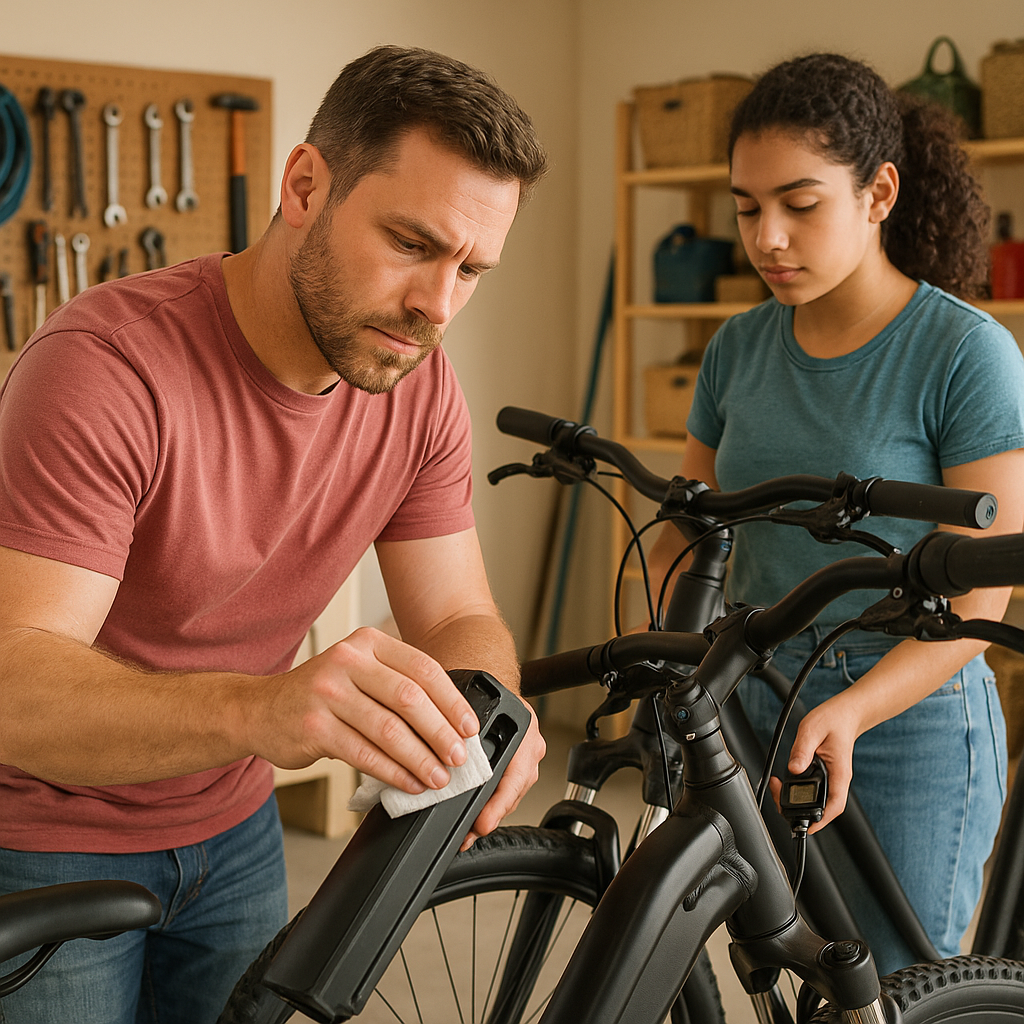
These expensive components benefit from proper handling:
- Store batteries at 40-80% charge when not used for extended periods (never completely drained)
- Avoid exposing batteries to extreme temperatures (below freezing or above 100°F/38°C)
- Use only manufacturer-recommended chargers
- Follow charging cycles properly—many modern batteries benefit from regular partial charges rather than complete discharge cycles
- Remove the battery when transporting bikes on external car racks
- Clean battery contacts periodically with electronic contact cleaner
With proper care, quality lithium-ion batteries typically maintain 80% capacity through 500-1000 complete charge cycles (approximately 2-5 years of regular use).
Mechanical maintenance follows similar patterns to conventional bicycles but with several important distinctions:
- Tire pressure: E-bikes generally require higher pressures due to additional weight. Check weekly and maintain manufacturer-recommended PSI.
- Brake systems: Inspect pads monthly as higher speeds and weights accelerate wear. Hydraulic systems require periodic bleeding (typically annually).
- Drive systems: Check chain/belt tension and condition more frequently than on conventional bicycles. Mid-drive motors place additional stress on drivetrains, potentially requiring more frequent component replacement.
- Torque specifications: Critical fasteners, especially those securing motor and battery systems, must be tightened to exact specifications—neither too loose (safety risk) nor too tight (component damage).
Electrical system care ensures reliable operation. Periodically inspect wiring harnesses for damage, particularly at connection points and cable entry/exit locations. Keep all connections clean and protected from water intrusion. Some systems benefit from periodic software updates that may improve battery management, motor performance, or user interface functionality.
Professional service plays an important role in e-bike maintenance. While many mechanical tasks remain owner-accessible, specialized diagnostic equipment and technical training make dealer service advisable for:
- Annual comprehensive inspections
- Motor system diagnostics and tuning
- Battery analysis and reconditioning
- Control system software updates
- Warranty-related repairs
Many quality e-bike manufacturers offer connected diagnostic capabilities, allowing service centers to evaluate systems remotely before physical appointments. Establishing a relationship with a knowledgeable service provider familiar with your specific drive system provides valuable technical support throughout ownership.
Seasonal considerations affect maintenance scheduling. Before winter storage, perform comprehensive cleaning, apply frame protectant, and prepare batteries for lower-temperature conditions. Spring recommissioning should include mechanical safety checks, electronic system testing, and verification of all control functions before resuming regular use.
Conclusion
Electric bikes represent far more than a passing trend—they're reshaping personal transportation by combining the joy and simplicity of cycling with practical assistance that expands both range and accessibility. As we've explored throughout this guide, e-bikes offer compelling advantages across multiple dimensions: environmental benefits through reduced emissions, financial savings compared to automobile ownership, improved commuting experiences, increased accessibility for diverse riders, and meaningful health benefits despite motor assistance.
The e-bike ecosystem continues evolving rapidly, with advancing battery technology delivering greater range, smart systems providing enhanced rider feedback, and specialized designs addressing specific use cases from urban commuting to off-road adventures. This dynamic market offers exciting opportunities but also requires informed decision-making when selecting the right model for your needs.
Before making your purchase, take time to test ride multiple styles, clearly identify your primary usage scenarios, research brand reliability, and ensure local dealer support exists for your chosen model.
Once you've found your ideal electric bicycle, protect your investment through comprehensive security measures, proper maintenance, and safe riding practices.
Whether you're seeking a more sustainable commuting alternative, returning to cycling after years away, or simply wanting to extend your riding range and enjoyment, today's electric bikes offer accessible solutions to match virtually any need or preference. As infrastructure improvements like protected bike lanes and secure parking continue expanding in many communities, the practical benefits of e-bike ownership will only increase in the coming years.
Frequently asked questions
What is an electric bike and how is it different from a regular bike?
An electric bike (e-bike) includes a battery-powered motor that assists pedaling, making rides easier and faster compared to traditional bicycles.
How far can electric bikes go on a single charge?
Most electric bikes offer a range between 20–70 miles on a full charge, depending on battery size, terrain, rider weight, and assistance settings.
Are electric bikes safe?
Yes, e-bikes are safe when used properly; wearing helmets, following traffic laws, and investing in theft protection increases overall safety.
Do electric bikes require special maintenance?
They need the same basic care as regular bikes, with added attention to battery charging, electrical components, and regular professional check-ups.
What is the average cost of an electric bike?
Entry-level electric bikes start around $1,000, while high-end models can exceed $5,000, depending on features and brand.